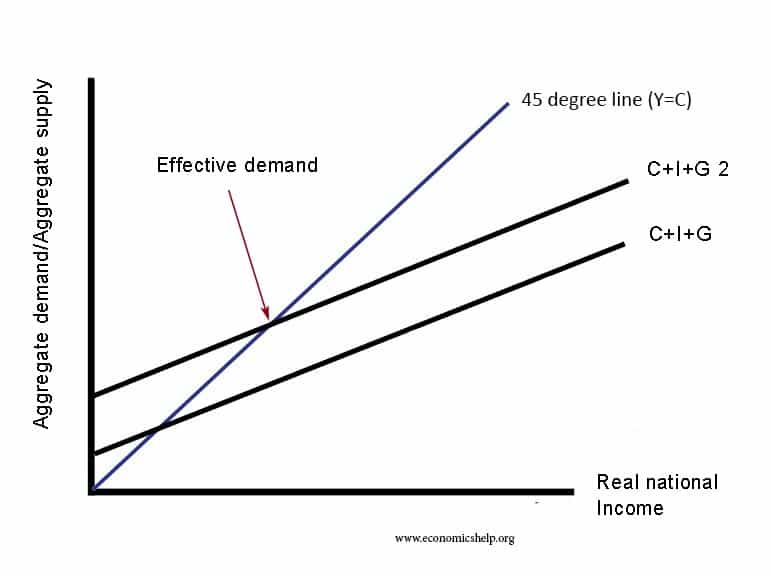
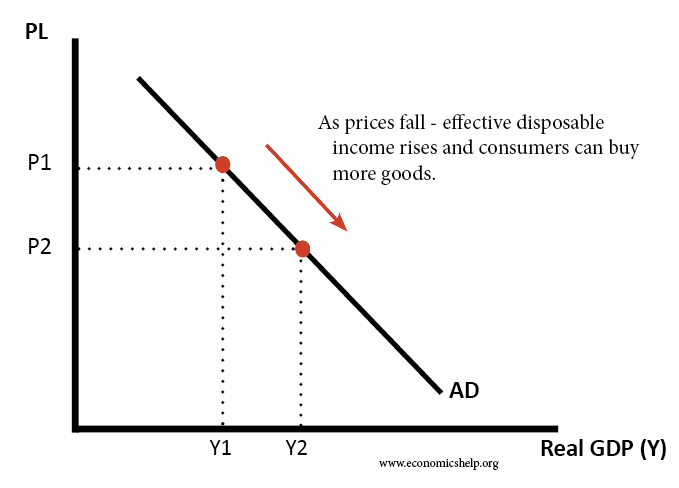
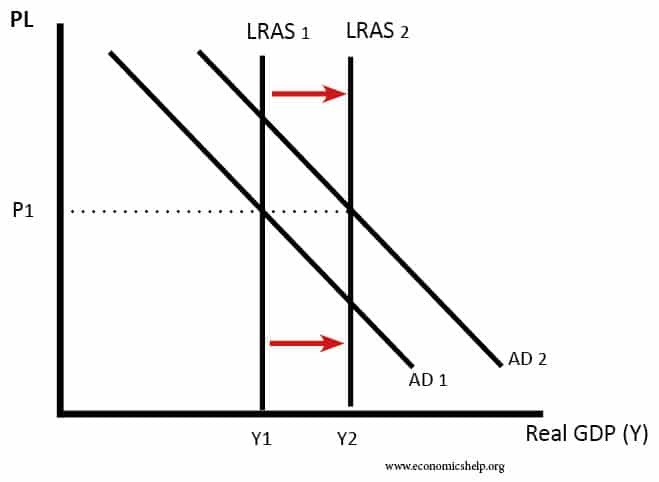
Effective demand
Effective demand refers to the willingness and ability of consumers to purchase goods at different prices. It shows the amount of goods that consumers are actually buying – supported by their ability to pay. Effective demand excludes latent demand – where the willingness to purchase goods may be limited by the inability to afford it …